Understanding skin ulcers: Causes, symptoms, risk factors and home remedies you must know |
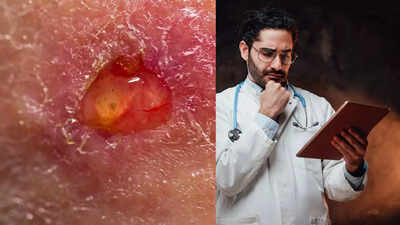
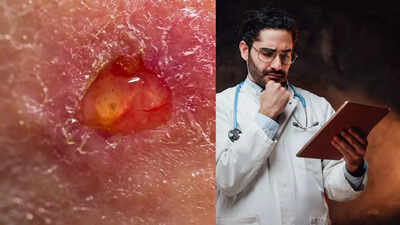
Skin ulcers are open, painful sores that occur when the skin and underlying tissues deteriorate, often due to poor blood circulation, prolonged pressure, or nerve damage. They most commonly develop on the legs, feet, hips, and back, though they can appear anywhere. Early symptoms include redness, swelling, tenderness, or discolouration, while advanced ulcers may form deep, crater-like wounds that can ooze fluid or become infected. Risk factors include diabetes, obesity, limited mobility, high blood pressure, smoking, and age-related circulation issues. Effective management involves identifying the underlying cause, improving blood flow, protecting the wound, and seeking timely medical care. Treatment may include dressings, antibiotics, compression therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery to promote healing and prevent complications.
Understanding skin ulcers and its symptoms
A skin ulcer is an open sore that forms when blood flow is impaired, preventing proper healing of the skin. Healthy blood circulation is vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues, which promotes wound repair. When circulation is compromised, even minor injuries can fail to heal and gradually develop into ulcers.Infected ulcers are particularly dangerous, as bacteria can spread from the wound into deeper tissues or the bloodstream, potentially causing serious complications. Skin ulcers are more common in older adults, affecting approximately three in every 1,000 people, with leg ulcers being the most prevalent.
Symptoms of skin ulcers
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the ulcer. Common signs include:
- Round or crater-like open sores
- Raised, thickened borders around the ulcer
- Red, warm, or discoloured skin in the affected area (shiny or blue in darker skin tones)
- Pain, tenderness, or itchiness
- Swelling around the ulcer
- Yellow or green pus if infection is present
- Changes in skin texture
In the early stages, skin discolouration and minor swelling may appear. As the ulcer progresses, it can exude fluid or blood, creating a moist, vulnerable wound.
Causes of skin ulcers
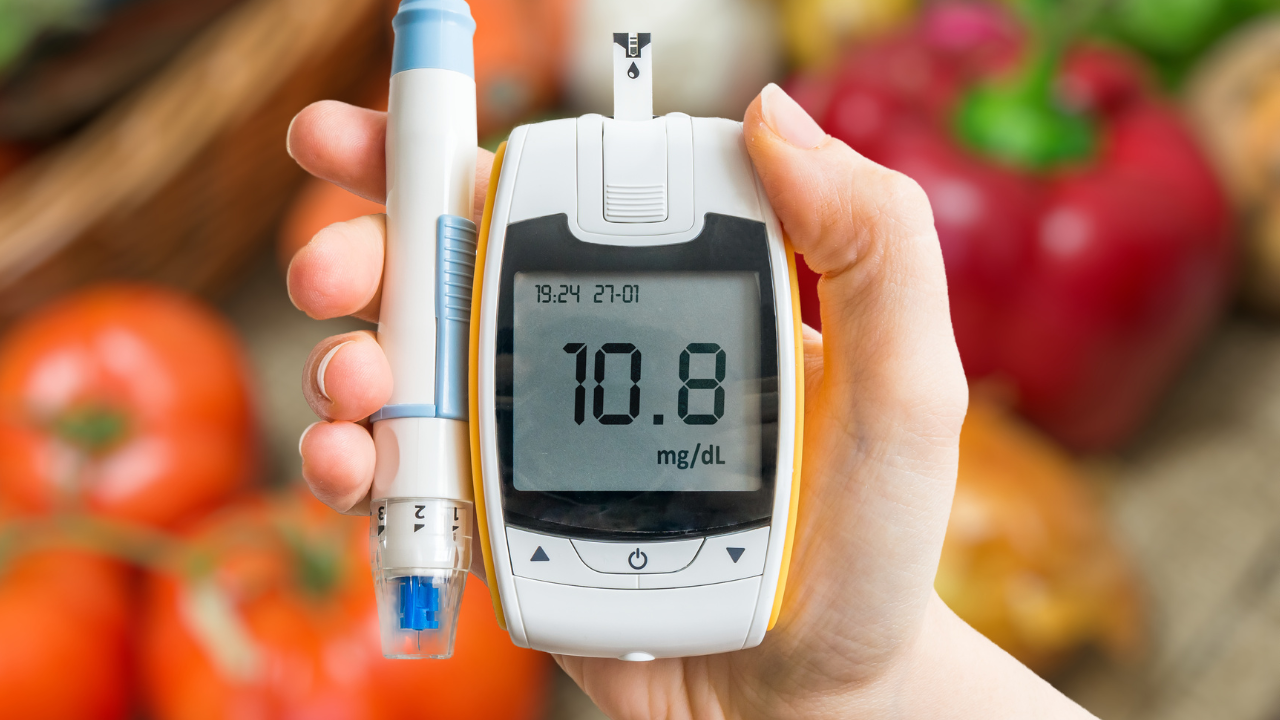
Skin ulcers develop primarily due to impaired blood circulation or prolonged pressure. Key causes include:DiabetesHigh blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy, leading to reduced sensation in the feet and legs. Injuries may go unnoticed, and slow wound healing increases the risk of ulcers.AtherosclerosisAlso called arteriosclerosis, this condition occurs when arteries narrow due to plaque buildup. Reduced blood flow can cause skin tissue breakdown, resulting in ulcers. Diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis.PressureContinuous pressure on the skin, often from prolonged immobility, compresses blood vessels and limits oxygen supply to tissues. Over time, this can cause pressure ulcers, commonly on bony areas like the heels, hips, and back.Venous insufficiencyWhen leg veins fail to return blood efficiently to the heart, it can lead to swelling and skin pressure. Conditions like varicose veins and blood clots can cause venous ulcers, most commonly between the knee and ankle.
Skin ulcers risks explained
Certain conditions and lifestyle factors increase the likelihood of developing skin ulcers:
- Pregnancy, due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume affecting veins
- Smoking, which damages arteries and disrupts circulation
- Limited mobility, such as being bedridden or using a wheelchair
- Age, as older adults are more prone to circulation issues
- High blood pressure and high cholesterol, which impair blood flow
- Obesity, raising the risk of diabetes and venous pressure
- History of blood clots
Home remedies for skin ulcers
For mild ulcers, home care can support healing, though severe cases require medical supervision:
- Leg elevation to improve blood flow
- Compression socks to reduce swelling and aid circulation
- Saline solution to gently clean mild ulcers
- Turmeric paste for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties
- Honey dressings for traditional wound healing benefits
When to seek medical helpIf a wound does not heal within two to three weeks, medical attention is crucial. Early intervention can prevent infections and other serious complications.Also Read | Lose belly fat in 30 days: Nutritionist reveals ‘magic drink’ that reduces bloating, and supports gut health