Working from home isn’t as efficient as you think: Here’s what the BLS ATUS 2024 data shows

New data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has revealed that employees working from home are logging significantly fewer hours than those based in offices. According to the 2024 American Time Use Survey (ATUS), remote employees worked an average of 5.14 hours per day compared with 7.79 hours for office-based staff. This represents a shortfall of 2.65 hours each day, equivalent to more than a full working day lost every week.The findings highlight a clear divide in productivity between remote and in-office employees. For many companies that adopted remote or hybrid models after the pandemic, the BLS data provides the most detailed evidence yet of how working arrangements influence time spent on actual job tasks.The gap between home and office work hoursThe BLS reported that in 2024, 87 per cent of full-time employed people worked on an average weekday, with an average of 8.4 hours worked. On weekends, only 29 per cent of full-time workers were on the job, averaging 5.6 hours. Among those working remotely, logged hours were consistently lower than those in traditional office environments.The 2024 ATUS results also showed that about 33 per cent of employed people spent time working at home on days they worked, a figure nearly unchanged from 35 per cent in 2023. However, the share of men working from home fell from 34 per cent in 2023 to 29 per cent in 2024, while the share of women remained steady at 36 per cent.Key Findings from the BLS ATUS 2024 Data
Gender and sectoral variationsGender-based differences were also visible. Men working remotely logged 12 minutes fewer per day than women, while in office settings men worked 18 minutes longer. These variations, according to the BLS data, suggest that work patterns at home may still be influenced by domestic and environmental factors.The BLS further identified differences across industries. Sectors such as construction, transportation and personal services showed steep declines in logged hours among remote workers, largely due to the nature of work. Construction employees working remotely, for example, reported only 2.17 hours of labour per day, compared with significantly higher averages among those on-site.
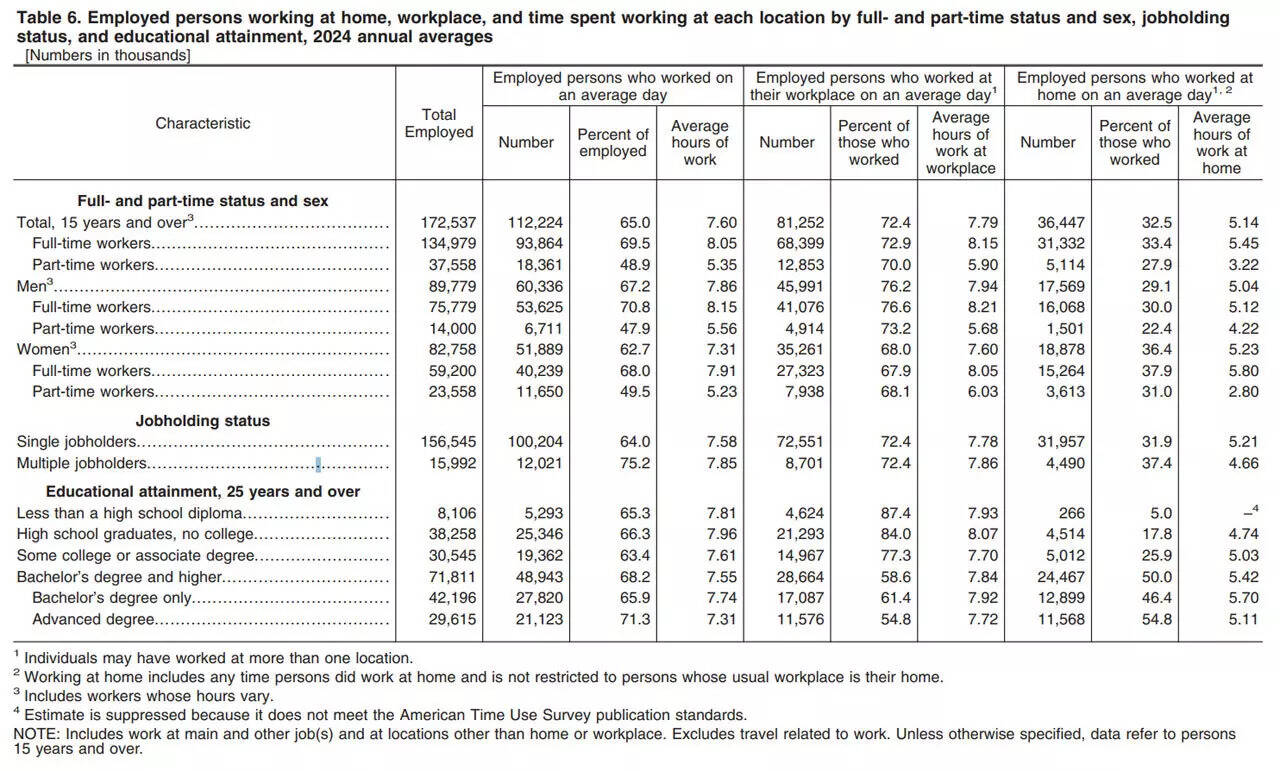
Education and workplace trendsAmong workers aged 25 and older, those with higher education levels were more likely to work from home. The BLS noted that 50 per cent of employees with a bachelor’s degree or higher worked some hours at home on days worked, compared with 18 per cent of those with only a high school diploma.In a statement quoted by the BLS, the ATUS report indicated that “time spent working” refers strictly to active job-related tasks rather than time spent connected to workplace systems. The survey results, as published by the BLS, provide a detailed statistical snapshot of how American employees distributed their working hours in 2024.